Heketi
Heketi provides a RESTful management interface which can be used to manage the life cycle of GlusterFS volumes. With Heketi, cloud services like OpenStack Manila, Kubernetes, and OpenShift can dynamically provision GlusterFS volumes with any of the supported durability types. Heketi will automatically determine the location for bricks across the cluster, making sure to place bricks and its replicas across different failure domains. Heketi also supports any number of GlusterFS clusters, allowing cloud services to provide network file storage without being limited to a single GlusterFS cluster.”
Reference: https://github.com/heketi/heketi
Overview
Create Volume
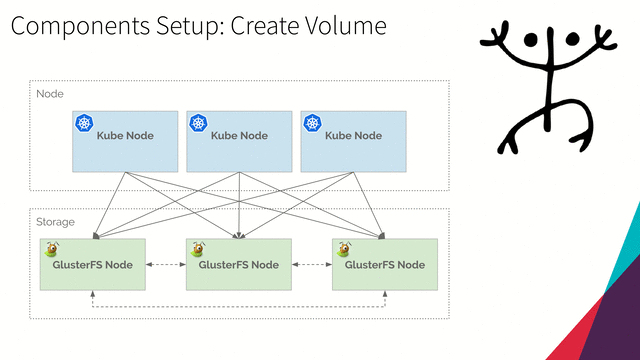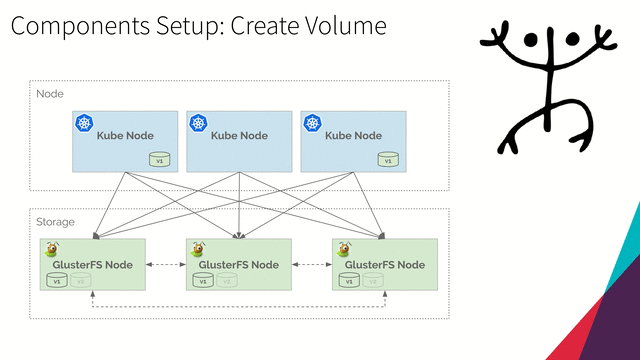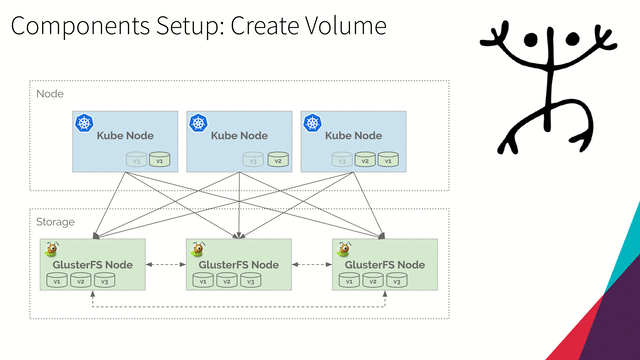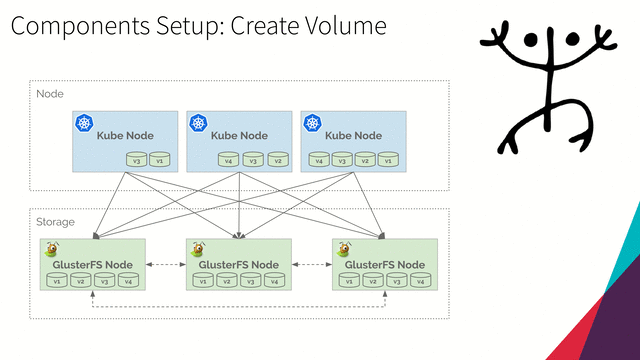
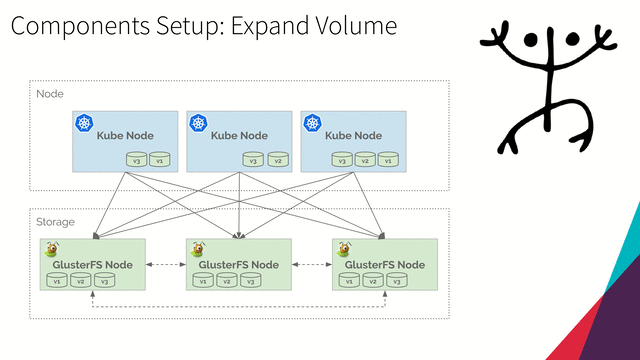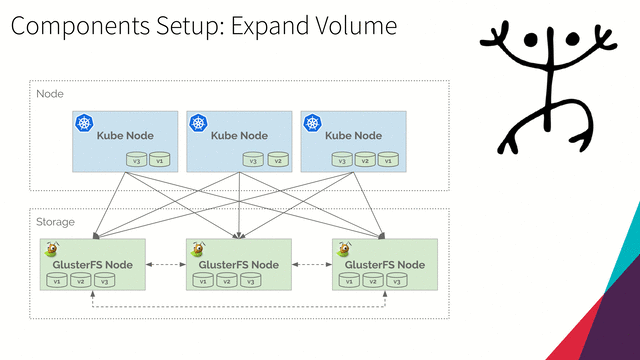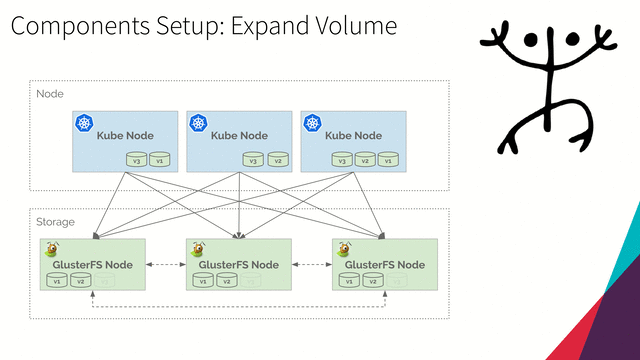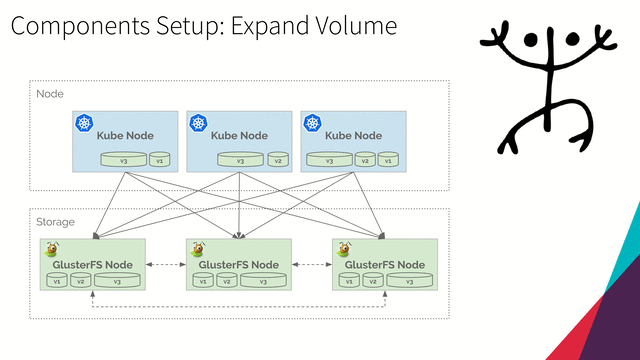
Expand Volume
Set up Heketi Rest URL in Storage Class
“So basically I have updated /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml by adding dnsPolicy: ClusterFirstWithHostNet and restarted kubelet.” - Thanks BostjanBozic!!
Patch file kube-controller-manager-patch:
--- kube-controller-manager.yaml 2019-05-06 05:32:38.212961105 -0300
+++ kube-controller-manager-patch.yaml 2019-05-06 05:32:14.380556753 -0300
@@ -65,6 +65,7 @@
- mountPath: /usr/share/ca-certificates
name: usr-share-ca-certificates
readOnly: true
+ dnsPolicy: ClusterFirstWithHostNet
hostNetwork: true
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
volumes:
-
Apply patch
/etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yamlon master nodes. This will change the static podkube-controller-managerconfiguration by addingdnsPolicy.ssh debian@kube-mast01.kube.demo sudo su - curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mvallim/kubernetes-under-the-hood/master/master/kube-controller-manager-patch -o kube-controller-manager-patch patch --no-backup-if-mismatch /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml < kube-controller-manager-patchssh debian@kube-mast02.kube.demo sudo su - curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mvallim/kubernetes-under-the-hood/master/master/kube-controller-manager-patch -o kube-controller-manager-patch patch --no-backup-if-mismatch /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml < kube-controller-manager-patchssh debian@kube-mast03.kube.demo sudo su - curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mvallim/kubernetes-under-the-hood/master/master/kube-controller-manager-patch -o ube-controller-manager-patch patch --no-backup-if-mismatch /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-controller-manager.yaml < kube-controller-manager-patchReference: https://github.com/gluster/gluster-kubernetes/issues/570
Install
Full reference: https://github.com/gluster/gluster-kubernetes
Deploy
-
Run
git clone https://github.com/gluster/gluster-kubernetes.gitThe response should be:
Cloning into 'gluster-kubernetes'... remote: Enumerating objects: 16, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (16/16), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (11/11), done. remote: Total 2515 (delta 5), reused 14 (delta 5), pack-reused 2499 Receiving objects: 100% (2515/2515), 1.08 MiB | 1.72 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (1334/1334), done. -
Edit config
This takes the form of a topology file, which describes the nodes present in the GlusterFS cluster and the block devices attached to them for use by heketi. A sample topology file is provided. When creating your own topology file:
-
Make sure the topology file only lists block devices intended for heketi’s use. heketi needs access to whole block devices (e.g. /dev/sdb, /dev/vdb) which it will partition and format.
-
The
hostnamesarray is a bit misleading.manageshould be a list of hostnames for the node, butstorageshould be a list of IP addresses on the node for backend storage communications.
-
Create a topology file:
cd gluster-kubernetes/deploy cp topology.json.sample topology.json -
Resolve hostnames of Gluster Nodes:
host glus-node01.kube.demo host glus-node02.kube.demo host glus-node03.kube.demoThe responses should be:
glus-node01.kube.demo has address 192.168.3.182glus-node02.kube.demo has address 192.168.3.96glus-node03.kube.demo has address 192.168.3.103 -
Change copy file
topology.jsonlike that:{ "clusters": [ { "nodes": [ { "node": { "hostnames": { "manage": [ "glus-node01.kube.demo" ], "storage": [ "192.168.3.182" ] }, "zone": 1 }, "devices": [ "/dev/sdb" ] }, { "node": { "hostnames": { "manage": [ "glus-node02.kube.demo" ], "storage": [ "192.168.3.96" ] }, "zone": 1 }, "devices": [ "/dev/sdb" ] }, { "node": { "hostnames": { "manage": [ "glus-node03.kube.demo" ], "storage": [ "192.168.3.103" ] }, "zone": 1 }, "devices": [ "/dev/sdb" ] } ] } ] }
-
-
Create namespace
glusterfs:kubectl create namespace glusterfsThe response should be:
namespace/glusterfs created -
Deploy
Next, run the
gk-deployscript from a machine with administrative access to your Kubernetes cluster. You should familiarize yourself with the script’s options by runninggk-deploy -h. Some things to note when running the script:- By default it expects the topology file to be in the same directory as itself. You can specify a different location as the first non-option argument on the command-line.
- By default it expects to have access to Kubernetes template files in a subdirectory called
kube-templates. Specify their location otherwise with-t. - By default it will NOT deploy GlusterFS, allowing you to use heketi with any existing GlusterFS cluster. If you specify the -g option, it will deploy a GlusterFS DaemonSet onto your Kubernetes cluster by treating the nodes listed in the topology file as hyper-converged nodes with both Kubernetes and storage devices on them.
- If you use a pre-existing GlusterFS cluster, please note that any pre-existing volumes will not be detected by heketi, and thus not be under heketi’s management.
Run the following commands to deploy Heketi:
./gk-deploy \ --user-key heketi \ --admin-key heketi \ --ssh-keyfile ~/.ssh/id_ed25519aaa \ --ssh-user debian \ --cli kubectl \ --no-object \ --templates_dir ./kube-templates \ --namespace glusterfs topology.jsonConfirm question
YThe response should be (if you are using kubectl < 1.13. Otherwise ou get a error, but it doesn’t affect the deploy Heketi. See here):
```text Using Kubernetes CLI. Using namespace “glusterfs”. Checking for pre-existing resources… GlusterFS pods … not found. deploy-heketi pod … not found. heketi pod … not found. gluster-s3 pod … not found. Creating initial resources … serviceaccount/heketi-service-account created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/heketi-sa-view created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/heketi-sa-view labeled OK secret/heketi-config-secret created secret/heketi-config-secret labeled service/deploy-heketi created deployment.extensions/deploy-heketi created Waiting for deploy-heketi pod to start … OK Creating cluster … ID: d266913187b2c860384a45c701ac16f4 Allowing file volumes on cluster. Allowing block volumes on cluster. Creating node glus-node01.kube.demo … ID: 90d62b5813ec436a06a55369179afbc4 Adding device /dev/sdb … OK Creating node glus-node02.kube.demo … ID: 54459c9f00d63b3f7c7b498e1230092c Adding device /dev/sdb … OK Creating node glus-node03.kube.demo … ID: 22b73b9fc98664bf5c4308274b919e71 Adding device /dev/sdb … OK heketi topology loaded. Saving /tmp/heketi-storage.json secret/heketi-storage-secret created endpoints/heketi-storage-endpoints created service/heketi-storage-endpoints created job.batch/heketi-storage-copy-job created service/heketi-storage-endpoints labeled pod “deploy-heketi-577fd694cb-42t9m” deleted service “deploy-heketi” deleted deployment.apps “deploy-heketi” deleted replicaset.apps “deploy-heketi-577fd694cb” deleted job.batch “heketi-storage-copy-job” deleted secret “heketi-storage-secret” deleted service/heketi created deployment.extensions/heketi created Waiting for heketi pod to start … OK
heketi is now running and accessible via http://10.244.5.9:8080 . To run administrative commands you can install ‘heketi-cli’ and use it as follows:
# heketi-cli -s http://10.244.5.9:8080 –user admin –secret ‘
' cluster list You can find it at https://github.com/heketi/heketi/releases . Alternatively, use it from within the heketi pod:
# kubectl -n glusterfs exec -i heketi-74ddc88bd6-mv65m – heketi-cli -s http://localhost:8080 –user admin –secret ‘
' cluster list For dynamic provisioning, create a StorageClass similar to this:
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: glusterfs-storage provisioner: kubernetes.io/glusterfs parameters: resturl: “http://10.244.5.9:8080”
Deployment complete!
5. Query the list of Pod of Heketi is running:
```shell
kubectl get pods -n glusterfs
The response should be:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
heketi-74ddc88bd6-mv65m 1/1 Running 0 3m37
-
Query the list of Gluster Cluster is running:
kubectl -n glusterfs exec -i heketi-74ddc88bd6-mv65m -- heketi-cli --user admin --secret heketi -s http://localhost:8080 cluster listThe response should be:
Clusters: Id:f9a5eaedce718d176f74e2bb7e3455c0 [file][block]
Configure Storage Class
StorageClass manifest:
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: glusterfs-storage
provisioner: kubernetes.io/glusterfs
allowVolumeExpansion: true
reclaimPolicy: Retain
parameters:
resturl: "http://heketi.glusterfs.svc.cluster.local:8080"
restauthenabled: "true"
restuser: "admin"
secretNamespace: "default"
secretName: "heketi-secret"
volumetype: "replicate:3"
-
Run the following commands to create storage class:
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mvallim/kubernetes-under-the-hood/master/heketi/gluster-storage-class.yamlThe response should be:
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/glusterfs-storage created -
Query the list of storage class:
kubectl get storageclassThe response should be:
NAME PROVISIONER AGE glusterfs-storage kubernetes.io/glusterfs 17s -
The provided secret must have type
kubernetes.io/glusterfs, Created in this way:kubectl create secret generic heketi-secret --type="kubernetes.io/glusterfs" --from-literal=key='heketi' --namespace=defaultThe response should be:
secret/heketi-secret created
Create Volume Claim
PersistentVolumeClaim manifest:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: persistent-volume-0001
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: glusterfs-storage
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 2Gi
-
Run the following command to create PersistentVolumeClaim:
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mvallim/kubernetes-under-the-hood/master/heketi/persistent-volume-claim.yamlThe response should be:
persistentvolumeclaim/persistent-volume-0001 created -
Query the list of persistent volume claim:
kubectl get persistentvolumeclaimThe responses should be:
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE persistent-volume-0001 Bound pvc-8dc0ce07-6e08-11e9-b6f1-0800276f613b 2Gi RWX glusterfs-storage 31s -
Query the list of persistent volume:
kubectl get persistentvolumeThe responses should be:
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE pvc-8dc0ce07-6e08-11e9-b6f1-0800276f613b 2Gi RWX Retain Bound default/persistent-volume-0001 glusterfs-storage 31s
Expand Volume
-
Run the following command to get persistent volume claim manifest of
persistent-volume-0001:kubectl get persistentvolumeclaim persistent-volume-0001 -o yaml > persistent-volume-claim.yamlThe output file
persistent-volume-claim.yamlshould be:apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: annotations: pv.kubernetes.io/bind-completed: "yes" pv.kubernetes.io/bound-by-controller: "yes" volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: glusterfs-storage volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-provisioner: kubernetes.io/glusterfs creationTimestamp: "2019-05-04T01:04:22Z" finalizers: - kubernetes.io/pvc-protection name: persistent-volume-0001 namespace: default resourceVersion: "67990" selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/default/persistentvolumeclaims/persistent-volume-0001 uid: 8dc0ce07-6e08-11e9-b6f1-0800276f613b spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany dataSource: null resources: requests: storage: 2Gi volumeMode: Filesystem volumeName: pvc-8dc0ce07-6e08-11e9-b6f1-0800276f613b status: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany capacity: storage: 2Gi phase: Bound -
Edit file and change
specresource storage to10Gi:Part of file
persistent-volume-claim.yamlspec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany dataSource: null resources: requests: storage: 10Gi -
Apply the persistent volume claim from the following
persistent-volume-claim.yamlfile:kubectl apply -f persistent-volume-claim.yamlThe response should be:
Warning: kubectl apply should be used on resource created by either kubectl create --save-config or kubectl apply persistentvolumeclaim/persistent-volume-0001 configured -
Query the list of persistent volume claim:
kubectl get persistentvolumeclaimThe response should be:
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE persistent-volume-0001 Bound pvc-8dc0ce07-6e08-11e9-b6f1-0800276f613b 10Gi RWX glusterfs-storage 4m2s -
Query the list of persistent volume:
kubectl get persistentvolumeThe response should be:
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE pvc-8dc0ce07-6e08-11e9-b6f1-0800276f613b 10Gi RWX Retain Bound default/persistent-volume-0001 glusterfs-storage 5m6s
Cleaning up
-
Run the following commands to delete
PersistentVolumeClaimandPersistentVolume:kubectl delete persistentvolumeclaim persistent-volume-0001 kubectl delete persistentvolume pvc-8dc0ce07-6e08-11e9-b6f1-0800276f613bThe responses should be:
persistentvolumeclaim "persistent-volume-0001" deletedpersistentvolume "pvc-8dc0ce07-6e08-11e9-b6f1-0800276f613b" deleted -
Query the list of
PersistentVolumeClaimandPersistentVolume:kubectl get persistentvolume kubectl get persistentvolumeclaimThe responses should be:
No resources found.No resources found.